How can you grow enough food for self-consumption and sale within urban areas? In this blog article, we will discuss various vertical farming methods that are available for cheap food growing for urban people.
Urbanization is a key threat to food security. As more people migrate to towns, they buy small residential plots that are uneconomical for food production and mechanization. Besides it had led to people converting once productive arable land tracts into high-rise apartments. Luckily, there are new farming technologies in urban agriculture like vertical farming that help urbanites to grow excess food right in towns.
If you are looking to learn more about this topic, we will cover the following details.
Methods of vertical farming

Are you wondering how you can grow food and other crops using vertical farming? This section details the common methods of vertical farming used around the world. They include hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics. These will allow you to grow food in liquid solutions, air, or mist environments without a soil medium and little water. Besides growing vegetables, you can grow fish and other marine life.
Related: 5 Smart farming ideas beyond Covid-19
What is vertical farming? Simply put, Vertical farming is a way of growing and harvesting crops on shelves or towers that you position vertically to maximize space. The difference from traditional farming is that you can get higher profits and yields. Plants grow on cups or containers to save space. The types of vertical farming you can grow this food are:
- Hydroponics
- Aeroponics
- Aquaponics
Hydroponics
As the name, hydro means, this type of vertical farming involves submerging plant roots in liquid solutions made of water and fertilizer or plant nutrients. Hydroponics is the most common form of soil-less farming. The key plant nutrients used in water solutions are calcium nitrate, potassium phosphate, and magnesium sulfate. You may fortify the solution with boron, chlorine, copper, iron, manganese sodium, zinc, and molybdenum. Besides, you can add nickel, cobalt, and silicon.
Aeroponics
Aeroponics farming systems grow on moist air or mist. You will suspend the plant roots in moist air that has fine sprayers that constantly supply it with a nutrient-rich solution. The system is the most efficient if you want to conserve water. Studies show that it uses 90% less water than hydroponics. Besides, it uses less than 60% of fertilizers while getting 45-75% more yields. In addition, these crops observe more minerals making the plants healthier and nutritious.
Aquaponics
The Aquaponics farming method combines raising fish in tanks or ponds combined with aquaculture crop farming. Fish waste from tanks supplies high nutrient content for crops placed in growing trays. The plant roots act as a natural filter for the water in which fish live. The bacteria that are present in the growing bed convert ammonia into nitrites, then nitrate biofertilizers.
Types of Vertical Farming
Are you considering which are the best places to start for your vertical farm? Vertical farming companies and individuals stack their crops in layers on skyscrapers, walls shipping containers, or abandoned warehouses.
Abandoned buildings
You can utilize an abandoned building like a warehouse to run your vertical farm. Some investors construct special buildings for vertical farming. An example is people who make cheap mud houses to grow mushrooms. Besides, you can repurpose a less profitable residential commercial or livestock unit to grow crops using hydroponics or aeroponics farms. A vertical farming system can earn you an average of $ 41.16/square foot. According to facts. A hydroponic farm will profit about 60% of the time unlike a real estate business, which may go for months without tenants.
Skyscrapers
It involves growing food on residential and office high-rise buildings. You will place crop and aquaculture systems vertically on the building’s exterior. Examples are the Skyfarm in London UK or the plant scrapers in Linkoping Sweden. It is a modern technology from traditional landscaping ideas. Instead of placing ornamental baskets and pots for beauty, you will grow cheap and healthy food for tenants and occupants.
Shipping containers
If you have limited space, you can consider stacking old shipping containers on top of each other. These are best for growing indoor plants, sprouts, and micro greens using LED light bulbs. Recycled shipping containers may be cheaper to start a vertical farm compared to building a different house. You can easily place lighting, heating, and ventilation structures for environmental control.
Deep farms
Deep farms are what you would consider as an underground farm. It is the best method to rehabilitate abandoned mining shafts or tunnels. Compared to on-surface vertical farms are cheaper. This is because temperature and humidity are more constant and require little energy to maintain. You can get 7-9 times more food in an underground farm than a conventional farm for a similar piece of land.
Smart Greenhouses
Smart farming technology like sensors and IoT can help you set up smart greenhouses. You can control the enclosure’s environmental factors for optimal growing conditions. You will control airflow, temperature, light, and moisture or plant nutrition. You will then place your hydroponic, geoponics, or aquaponics farm inside. A smart greenhouse can be made of glass, ultraviolet-treated polyethylene, or other translucent equipment.
Best crops of soilless farming
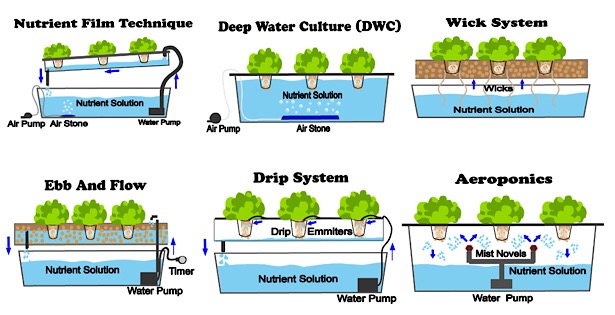

Whether you are looking for food or profits the following are possible crop and fish ideas for vertical farmers. To include them in your farm look into profits potential, low operation costs, and the food’s nutritional value.
Leafy greens like lettuce, herbs, and commercial flowers are the most common for hydroponic system farmers. Others focus on growing baby greens, sprouts, and microgreens like wheatgrass in those vertical farms. The microgreens are fast-growing and ready to harvest in 10-14 days. The list of possible plants you can grow is endless. It includes light vines like strawberries and greens like lettuce, kale, and basil. To Make an informed decision based on market research and advice.
If you want an aquaponics farming system that combines crops and fish farming, bass, tilapia, and barramundi fish species are best to rear. Other profitable aquatic organisms you can rear in indoor tanks are snails, crayfish, and prawns. Some edible algae, seaweed, and seaweed are other options.
Indoor farmers can farm edible mushrooms, the highly valuable silk, or other insects like termites and cockroaches. Some of these have low acceptance as food among many communities in the country. They have a huge demand in medical, research, and industrial use.
Pros and cons of vertical gardening


Is vertical farming ideal for you? To decide, compare its benefits and cons regarding profits, health, and other factors.
Pros of vertical farming
- Stable crop yields and profits throughout different weather and season conditions since crops will grow in controlled environment conditions.
- Fewer crop losses since crops and fish farms are protected against animals & pests and invasive plant species.
- Polyculture benefits or ability to grow all kinds of plants in different towers or rows.
- Savings in water since the systems are over 60% more efficient in water Use.
- Vertical farming can be fully organic where you use bio fertilizers and bio pesticides raising more quality and safe foods.
- Vertical farming can reduce food imports from rural areas and other countries.
- Vertical farms are more efficient on land use and reduce habitat destruction for farms.
- Other benefits like clean or green energy generation and conservation by the use of smart LED bulbs.
Cons of vertical gardening
- Expensive to start and run since it needs experts to run a vertical farm project.
- High upfront costs to buy expensive technology and materials like sensors and monitors.
- Significant operational from high-energy consumption to control temperatures, humidity, and ventilation in controlled environments.
- May need expensive permissions and licenses to establish like the underground tunnels and mines.
- Technology is at a nascent stage in the region with an underdeveloped market for inputs and outputs. Infrastructure regarding the processing of crops is missing.
- Only suitable for certain kinds of plants like lightweight veins and microgreens.
- Plants may contain fewer nutrients due to a lack of natural sunlight and nutrients from the soil. Its success will lead to lost livelihoods for farmers in rural areas.
How to start soilless farming
In our conclusion, we look at what you need to start investing in vertical farming. Start by investing more in research and market analysis to identify the best type, crops, and market for your crop and/or fish products. Once you have identified, shop for required farm inputs to get quality yields.
There are various farm inputs you need for a vertical farm. You can buy them from a farm shop near you or buy the best quality from an online E-commerce like Amazon.
Hydroponics garden startup kit list
- Plant clips
- Pvc pipes
- Plastic tubing
- Plant-growing materials like coco peat
- A nutrient water tank
- Planting cups or trays
- Stand and trellis made of PVC pipe
- Fertilizers for a hydroponic system
- A water pump
- Plants seeds or seedlings
- Twines
- Water pH testing kit




